Engine performance is an engine’s ability to do work in terms of horsepower, torque, or efficiency.

Engine Performance Parameters
- Mean Effective Pressure
- Mean Piston Speed
- Specific Power Output
- Specific Fuel Consumption
- Air-Fuel Ratio
- Calorific Value of the Fuel
Mean Effective Pressure (pm)
The average pressure inside the cylinders of the internal combustion engine is based on the resulted power output.
For any engine, there will be two Mean effective pressures. One is Specific Indicated Mean Effective Pressure(pim), and the second one is the Brake mean effective pressure (pbm). These two are derived from the indicated power and the brake power.

Mean Piston Speed
Mean Piston speed can be calculated from the following formula
Mean piston speed (Sp) = 2 × Stroke Length × Speed in RPM
Specific Power Output (Sp)
The specific Power output can be simply defined as the power output per unit area of the piston.
Specific Power output (Ps) = Brake Power/Piston Area
Air-Fuel Ratio
The proportions of the air with the fuel play a crucial role in the performance of the engine. This is expressed in the terms of the air-fuel ratio. In spark Ignition Engines, the Air-Fuel ratio will be the same for most of the operations. But in the Compression engines where the fuel is entered separately with the help of the fuel injectors, so that if the load needs to be increased, then the fuel amount will be increased directly in the cylinder.
Calorific Value (CV) of the Fuel
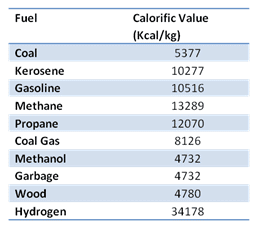
The calorific value of the fuel is defined as the amount of thermal energy released per unit quantity of fuel when it is burned completely.

Conclusion
We have discussed the different types of Efficiencies in the Internal Combustion Engine, and also the Engine Performance parameters such as the Mean Effective Pressure, Mean Piston Speed, Specific Power Output, Specific Fuel Consumption, Air-Fuel Ratio, Calorific Value of the Fuel. If you have any thoughts please let us know in the below comment section.